Welcome to Mattress Clarity’s comprehensive sleep dictionary! Here you’ll find explanations of all things sleep. Whether you’re looking for information on a disorder, want to know what REM sleep is, or want to learn a variety of sleep terms, you can find out here.
What are the Most Popular Sleep Terms?
 With work-from-home positions on the rise, the still-present coronavirus pandemic, and wellness trends impacting the way the world views sleep, we were curious to see how Google search for sleep-related terms was impacted over the past several years. Here’s what we found:
With work-from-home positions on the rise, the still-present coronavirus pandemic, and wellness trends impacting the way the world views sleep, we were curious to see how Google search for sleep-related terms was impacted over the past several years. Here’s what we found:
- Search volume for “Jet lag” was 84,925 in February 2020, just before the outbreak of COVID-19. This then decreased rapidly to 47,002 in April 2020, following the start of the pandemic.
- Search volume for “melatonin” and “insomnia” are closely related and tend to peak in January. Searches for “insomnia” peaked in April 2020 following the start of the coronavirus pandemic.
- “Sleep deprivation” also reached its highest monthly search volume of 84,716 during the early days of the pandemic in April 2020.
- Search volume for all sleep terms on our list was on the rise in the summer of 2022. Contrarily, previous years showed the greatest volume of search during lockdown periods and around January, which could be related to seasonal affective disorder as well as high rates of coronavirus infections.
Sleep Terms A-Z
Aromatherapy: An ancient practice and form of therapy that uses plant oils to relax and soothe. Smells from the oils travel to the brain and help calm the mind and body.
Artificial light: Light that has been created from any source other than the sun. Examples of artificial lights include lamps and candles.
Biphasic sleep: Sleep that is divided into two sessions per day. A biphasic sleeper might sleep for 5 hours at night, and take a 3-hour nap during the day. Though it occurs naturally for some, it’s more commonly caused by a sleep disorder.

Blue light: One of the colors of light on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though it is emitted by the sun (along with the other colors of the spectrum) it is also also given off artificially, by devices like smartphones and laptops. Though we need blue light to keep us alert and help our bodies produce melatonin, too much blue light, particularly artificial blue light at night, can mess with our circadian rhythm.
Brown noise: Sound that uses all the frequencies that the human ear can recognize. Similar to white noise, it can help listeners tune out and relax. However, unlike white noise, brown noise’s lower frequencies are slightly louder and higher frequencies are slightly softer. Those who suffer from ADHD, in particular, may find brown noise a helpful way to focus. Brown noise may sound like crashing waves or blowing wind.
Chronotype: A particular sleep pattern that an individual has. Depending on your chronotype, you’ll feel more alert at certain hours and tired at others. Morning people are one type of chronotype, and night owls are another.
Circadian rhythm: The body’s internal clock that runs for a typical period of 24 hours. It sets the body’s sleep and wake times and usually runs parallel to the rising and setting of the sun.

Cognitive function: Put simply, using one’s brain. Processes like remembering, problem solving, learning, and decision making are all parts of cognitive function.
Cognitive impairment: Occurs when a person can’t perform typical mental processes. It can affect only one process, like memory, or multiple, like decision making and thinking. It can be brought about from disease, trauma, or aging.
CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure): A form of obstructive sleep apnea therapy, a CPAP machine attaches to the nose and delivers air continuously while the user sleeps.
Deep sleep: The third stage in the sleep cycle, deep sleep, or slow wave sleep is the most restorative sleep phase. This sleep stage allows the body to repair itself, and is essential for proper functioning. It typically lasts for between 45 minutes and an hour and a half, and it’s hardest to wake up a sleeper when they are in this stage.
Delayed sleep phase syndrome: A circadian rhythm sleep disorder. It occurs when a sleeper’s sleep pattern is at least two hours beyond what is socially typical. This syndrome is most common in young adults, and symptoms may include struggling to wake up for school.
Dream: An altered conscious mental state that occurs during sleep. The images or experiences portrayed in a dream may be based on real memories or have more fantastical themes.
Excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS): Trouble staying awake and alert during daytime hours. EDS is commonly caused by sleep deprivation, insomnia, and sleep apnea. It can also be caused by certain medications.
Fatigue: A feeling of lethargy that lasts indefinitely. Fatigue can affect the body, mind, or both, and often presents as feeling tired or listless. Those with depression often experience fatigue.
Hypersomnia: A sleep disorder that makes it difficult to stay awake during the day, even if the person has gotten enough sleep at night. Hypersomnia sufferers might experience excessive daytime sleepiness and feel the need to take frequent naps throughout the day.

Insomnia: A sleep disorder that makes it hard to fall or stay asleep. It’s relatively common, affecting more than 60 million Americans per year. It can be short term, lasting only a few nights, or chronic, lasting months or even years. Though the exact cause is not known, factors like stress, excessive work, and health issues like cardiovascular disease can contribute to its occurrence.
Jet lag: Occurs when someone skips over multiple time zones, typically when flying. Their body clock will no longer be in sync with the time of day, and they may find themselves falling asleep or waking up too early or too late.
Light therapy: A form of therapy that uses artificial light to mimic natural light. Natural light has a number of positive benefits on mood, sleep, and overall wellness. Light therapy boxes can treat a number of conditions including seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and depression.
Long sleep: A type of hypersomnia in which people sleep more than others in their generational group. They may sleep an hour longer, or several hours longer.
Lucid dream: A dream in which the sleeper is conscious of the fact that they are dreaming. Lucid dreamers may be able to control what happens in their dreams.
Melatonin: A hormone that is released by the brain’s pineal gland. The body produces melatonin when it gets dark out. Melatonin signals to the body that it is time to sleep. It can be found in supplement form, and is used as a natural sleep aid.
Metabolism: The bodily processes that turn food into energy. This process allows the body to harness calories from food and turn them into fuel for keeping the body’s cells and tissues functioning. Metabolism functions constantly to keep the body running.
Microsleep: Very brief periods of sleep. Microsleep can occur in spurts of just 30 seconds or less. A number of sleep disorders can cause microsleep, including insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness, and narcolepsy.
Monophasic sleep: The most typical form of sleep, monophasic sleep refers to sleeping for just one period of time. Those who sleep through the night and don’t nap during the day are monophasic sleepers.
Nap: A brief period of sleep that is taken with intention, typically during daytime hours. Most experts recommend limiting naps to 20 to 30 minutes.
Narcolepsy: A sleep disorder that causes individuals to uncontrollably fall asleep for brief periods. Sufferers also experience cataplexy (sudden loss of muscle tone) and excessive sleepiness during the day. It is believed narcolepsy affects between 135,000 and 200,000 people in the US.

Natural light: Light that comes directly from the sun. The sun is the only source of natural light.
Night sweats: Excessive sweating that occurs during sleep. Though it is common to wake up hot and sweaty, the cause may be a room that’s too hot or stuffy pajamas and bedding. Real night sweats are caused by hot flashes. The sweats can be intense enough to soak pajamas and bedding. Night sweats can be related to health conditions like diabetes, or can be related to normal processes like menopause.
Night terror: A sleep disorder in which sleeping individuals wake up abruptly and scream, cry, and/or sleepwalk. Night terrors typically occur during REM sleep, which is the dream phase of sleep. They are more common in children and teens than adults.
Nightmare: A dream that has frightening or troublesome themes. Nightmares can lead to bad feelings upon waking up and are sometimes quite memorable.
Nocturnal: Active or activity that occurs during or throughout the night. Nocturnal animals, like bats, owls, raccoons, hunt during the night.
Non 24-hour sleep wake disorder: A type of circadian rhythm disorder in which an individual’s internal clock is not synchronized to the 24-hour time period of a full day and night. It can cause sleep and wake times to shift later or earlier, and if left untreated can lead to waking hours occurring during the night. This disorder is common in blind people.
Non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREM): The first cycles of sleep before REM sleep. NREM is typically divided into three phases of sleep, which last between 7 and 40 minutes, with stages 1, 2, and 3 each increasingly longer. NREM sleep is important for bodily repair and recovery.
Parasomnias: Sleep disorders that include physical symptoms like talking or walking. Parasomnias can occur while a person is asleep or just waking up. Examples of parasomnias include sleep walking, sleep talking, and night terrors.
Pink noise: Similar to white noise, pink noise is meant to relax and soothe. In pink noise, the higher tones are softer, which can make it sound more calming for some listeners.
Polysomnography: A test that measures sleep in some way. It can study how sleep affects the brain or the body. Polysomnographies are most often used to diagnose sleep disorders, particularly obstructive sleep apnea.
Power nap: A quick, short daytime sleep that helps a person feel more energized and able to complete tasks. Power naps typically range from about 10 to 30 minutes.
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep: The stage of sleep in which dreams occur. Like the name says, the eyes move rapidly under the eyelids during this sleep stage. REM sleep occurs after the first three non-REM (NREM) sleep stages. Most people will have between four and six REM stages per night.

Screen time: The amount of time one spends looking at or interacting with a screen, including phones, computers, and televisions.
Sedative: A drug that has a calming or sleep-inducing effect. They are often prescribed to patients with anxiety and/or sleep disorders. Examples of sedatives include benzodiazepines like Xanax and hypnotics like Ambien.
Shift work sleep disorder: A type of sleep disorder that occurs in individuals who have unusual work hours, like graveyard shifts or very late/very early shifts. It can make it more difficult to fall asleep at normal hours and to stay asleep throughout the night.
Short sleep: Sleep that only lasts for a brief period of time. Short sleep is similar to a nap and usually occurs outside of bed.
Sleep aid: A prescription drug or herbal supplement that helps promote sleep. Sleep aids include melatonin, valerian, Ambien, and Nyquil.
Sleep apnea: A type of sleep disorder in which sleepers stop breathing briefly throughout the night. It can be potentially dangerous, and even fatal, if left untreated. Sleep apnea can be obstructive or central. Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the airways are blocked, while central sleep apnea happens when the brain doesn’t properly tell the body to breathe.
Sleep architecture: The way that sleep patterns are typically organized. It includes the three NREM stages of sleep and REM sleep, and the multiple cycles of these stages that sleepers experience in a normal night of sleep.
Sleep cycle: A complete loop of the three phases of NREM sleep and one phase of REM sleep. A healthy night of sleep consists of four to six cycles of sleep.
Sleep debt: Similar to financial debt, sleep debt refers to the amount of sleep you owe (in this case, your body). Sleep occurs from sleeping too little sleep, be it from a sleep disorder or simply improper sleep scheduling. Sleep debt can increase over time and can lead to negative effects on the body and mind like grogginess, irritability, and confusion.
Sleep deprivation: Similar to sleep debt, it refers to a lack of proper sleep, which is between 7 and 9 hours for adults. Sleep deprivation can lead to a higher risk for serious health problems including heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
Sleep disorder: Any sleep-related issue that leads to poor-quality or poorly-timed rest. Common sleep disorders include insomnia, sleep apnea, narcolepsy, and restless leg syndrome. Sleep disorders have a range of causes including medications, anxiety, chronic pain, and respiratory issues.
Sleep hygiene: A routine and environment that promotes healthy sleep. Good sleep hygiene includes sticking to the same bedtime and wake up time, not looking at screens before bed, sleeping in a cool and dark room, and only using your bed for sleep and sex.
Sleep inertia: Difficulty transitioning from sleep to wakefulness. It can include feelings of grogginess and a strong desire to remain in bed. Sleep inertia can make it difficult to complete early morning tasks.
Sleep latency: The amount of time between getting into bed and falling asleep. A healthy person who is getting proper sleep should expect their sleep latency period to last between 10 and 20 minutes.
Sleep meditation: A type of meditation, or practice of clearing the mind and relaxing the body, that is meant to help induce sleep.
Sleep onset: The moment when you fall asleep. At the onset of sleep, the body moves from wakefulness to the first stage of sleep.
Sleep paralysis: Occurs after the body has been paralyzed by REM sleep. Sleepers will wake up, but find their body is unable to move. They may hallucinate dream-like images which can be frightening. It is most often seen in those with sleep apnea or narcolepsy, but anyone can experience it.
Sleep pattern: Related to circadian rhythm, sleep pattern refers to the body’s regulation of when it should be asleep and when it should be awake. A healthy sleep pattern for adults consists of 7 to 9 hours during the night. Sleep patterns can be affected by sleep disorders and lifestyle factors.
Sleep phase: A stage of the sleep cycle, which consists of three stages of non-REM sleep and one stage of REM sleep. Each of these stages is a sleep phase.
Sleep regression: Occurs when a baby who had previously been sleeping soundly begins to wake up and fuss throughout the night. Sleep regression typically lasts for between two and four weeks. It can have a number of causes, including growing pains, teething, and moving to a different sleep environment.
Sleep-wake cycle: The body’s biological clock that controls when it is meant to be awake and when it should sleep. The sleep-wake cycle is tied to the light and dark periods of the day.
Sleeping pill: A drug that is taken as a tablet, pill, or capsule that helps you fall asleep. Generally, sleeping pills are sedatives that must be prescribed by a doctor.
Sleeping position: The way in which a person sleeps. Sleeping positions include side sleepers, back sleepers, stomach sleepers, and combination sleepers, who switch between two or more positions throughout the night.
Slow-wave sleep: The deepest phase of sleep. Slow-wave sleep is the third Non-REM phase of sleep and occurs just before REM sleep. It takes between 70 and 90 minutes to complete this sleep phase. Slow-wave sleep is the most restorative sleep stage and helps the body heal and grow.
Snoring: A loud sound that comes from a sleeper when their airways are partially blocked. It is caused by tissues rattling together as air tries to pass through them. Snoring is more common in overweight and elderly people.
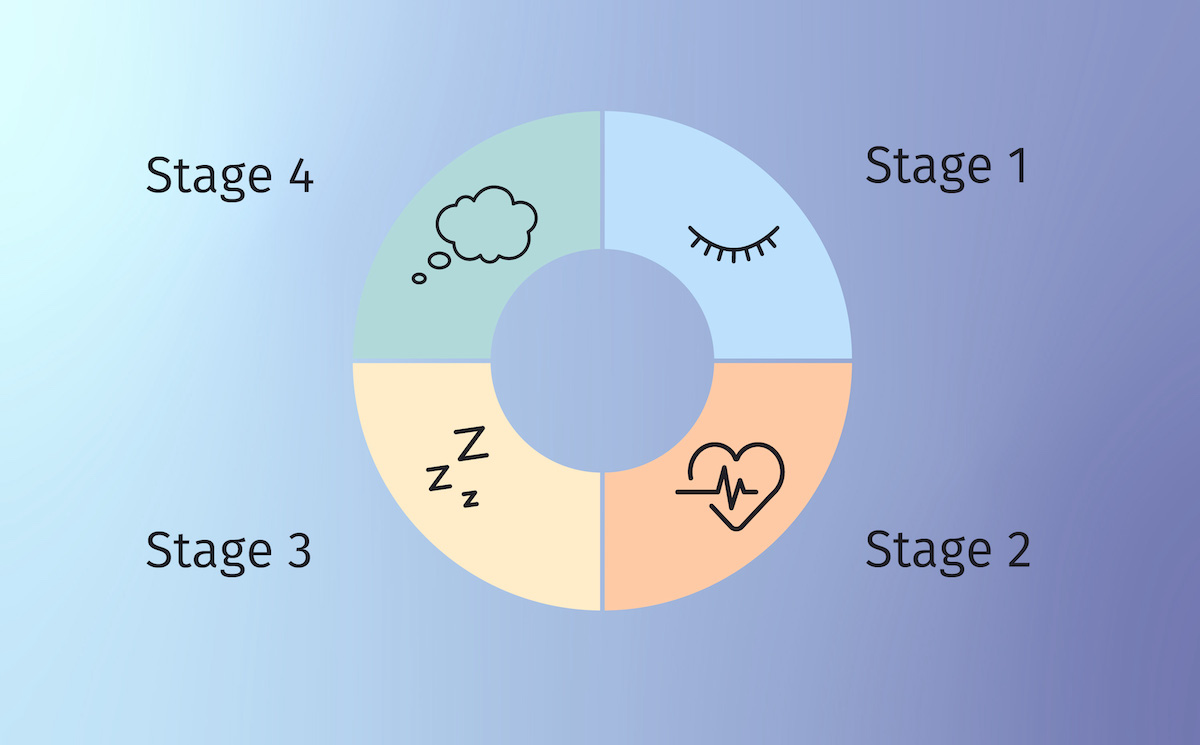
Stage 1 sleep: The first sleep stage, this stage happens right after the onset of sleep. It is a non-REM sleep stage, and typically lasts between 5 and 10 minutes.
Stage 2 sleep: The second sleep stage, this stage is also a non-REM phase and lasts about 20 minutes. During this stage, the heart rate slows, muscles relax, and the body’s temperature drops.
Stage 3 sleep: The third stage of sleep and the last non-REM phase, this stage lasts between 70 and 90 minutes. This is the deepest stage of sleep and most restorative. During this stage the mind consolidates memories and the body heals itself.
Stage 4 sleep: The final sleep stage in the sleep cycle, this stage is a rapid eye movement (REM) phase. Dreams occur during this stage, and while the body is paralyzed, the brain is highly active.
White noise: A noise that has many frequencies that are played simultaneously and at equal intensity. White noise typically sounds a bit like static, and is meant to help calm or reduce other noise pollution.

